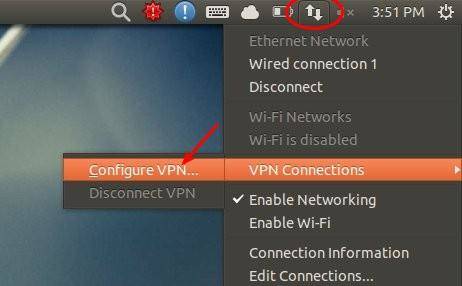
Yesterday, I finally managed to install Cisco VPN client for Linux on my main home workstation, running Ubuntu 10.04. Though, I'm still troubleshooting connection issue with our service provider, I believe I'm one step further of true, Windows free workstation running on ASROCK mini. Once installed, you can follow below steps to setup Cisco VPN for Ubuntu. 1.) Move your cursor to right-top corner system tray area, click on Network Manager icon and choose VPN Connections - Configure VPN.

These instructions are for installing and using the Cisco AnyConnect client on Linux and have been tested with:
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
- Here’s the simple steps for you to connect to a Cisco VPN in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. Cisco, an American company is the leading provider and manufacturer of enterprise network devices, telecommunication hardware, networking security and networking software. According to computer profile as of April 2018, Cisco holds a 73.9% market which makes it the.
- Although there is a native Linux client offered by Cisco, it is not very well supported, and in some cases the user does not have access to the client. Fortunately, there is a simple solution to this problem – thanks to OpenConnect. OpenConnect is a client for Cisco’s AnyConnect VPN. It is free software, and is released under the GNU LGPL.
Other versions of Linux are known to support the Cisco AnyConnect client but have not been fully tested by ComTech. OpenVPN may also work as an alternative to the Cisco AnyConnect client but is not a supported configuration.
Installation
- Download the installation file.
- Uninstall any previous versions of the AnyConnect client, using the uninstall script by running:
sudo /opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn_uninstall.sh - Untar the gzip’d tar file, which creates a directory that begins with:
anyconnect - cd into the anyconnect directory.
- cd into the vpn directory.
- Install the VPN with the command:
sudo ./vpn_install.sh
Using the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client
To Connect with the NC State VPN with Duo
To Disconnect
- Click on the Cisco AnyConnect icon.
- In the Connection tab:
Click on Disconnect.
VPN setup in Ubuntu – General introduction
VPN (Virtual Private Network) lets you establish a secure connection over the non-secure Internet, e.g. from a notebook to an office server.
Getting a VPN to work requires general knowledge on networks, and it may require some specific knowledge on routers, firewalls and VPN protocols.
In order to use VPN on Ubuntu, you need to make sure that support for the required VPN protocol is installed. Several VPN protocols exist:
PPTP (Microsoft VPN)
Cisco VPN
OpenVPN
IPSec VPN
Not covered on this page, so far
Usage
- Click on the network-manager in the system tray
Choose VPN Connections -> Configure VPN
- Click Add
You might have to restart the network-manager to get the added VPN connection on the list (killall nm-applet; nm-applet &)
- Now the VPN connection should be shown in the network-manager
VPN setup in Kubuntu Feisty (7.04)
You have to install the additional package
Please refer to WifiDocs/NetworkManager under VPN support for more information.
VPN setup using the command line
Run the following:
Create file /etc/ppp/peers/YOUR_COMPANY with this content:
Add to /etc/ppp/chap-secrets:
Create file /etc/ppp/ip-up.d/add-subnet with content similar to:
In the above line, adjust subnet values (192.168.100.0/24) if needed
Then run:
- Connect to VPN: sudo pon YOUR_COMPANY To disconnect, press Ctrl+C or close the terminal.
- If you do not want to see VPN connection debug output, in file /etc/ppp/peers/YOUR_COMPANY delete 3 lines: debug nodetach logfd 2
In this case, “pon YOUR_COMPANY” will run as a background process. Use “poff YOUR_COMPANY” to disconnect.
VPN setup in Ubuntu 8.10
I stole these instructions written by mgmiller from http://ubuntuforums.org/showpost.php?p=7089396&postcount=196. This is for connecting to a Microsoft VPN.
Cisco Vpn Client For Linux Ubuntu 18.04
- You need to install 2 packages:
- network-manager-pptp
- pptp-linux
- input the IP address of the target computer.
- input your user name. Leave all else blank, unless you are tunneling to a domain, then enter the domain name where indicated.
- hit Advanced button.
- UNcheck PAP (because PAP means to allow unsecured passage - this is the source of 'no shared shared secrets')
- Check CHAP, MSCHAP and MSCHAPv2.
- Check Use Point-to-point encryption (MPPE)
- Select 128-bit (most secure).
- Check Allow stateful encryption.
VPN setup in Ubuntu 9.04
I could not get any VPN working on 9.04. There appears to be some bugs in the configuration tools, you may be able to get things to work via the command line.
VPN setup in Ubuntu 9.10
The following instructions were originally written by sweisler at http://ubuntuforums.org/showpost.php?p=8261958&postcount=6. They have been additionally tested for PPTP to an MS VPN:
- Here's a synopsis of my VPN setups. I have proven this to work on both x86 and x64 for all 3 VPN types. Important note/disclaimer: I tested these configurations on VMware Workstation 7 VM's and a Dell Vostro 220. All installations were fresh installs, not upgrades. Also, please notice that I detail what type of firewall/VPN I am connecting to for each VPN type. There are so many variations on these VPN implementations that it is extremely difficult to generalize a known-good configuration for each.
- Install various VPN components
- PPTP
- pptp-linux
- network-manager-pptp
- vpnc
- network-manager-vpnc
c. OpenConnect
- openconnect
- network-manager-openconnect
- PPTP
- Reboot
- PPTP VPN Configuration - This setup works for connecting to ISA 2004/2006 PPTP VPNs. It should work for connecting to MS PPTP VPN implementations in general. I can't speak for other PPTP VPN implementations.
- Create new PPTP connection
- VPN Tab Settings
- Set Connection name
- Set Gateway
- Set username (for domain-based user accounts, use domainusername)
- DO NOT SET PASSWORD
- DO NOT SET NT DOMAIN
- PPTP Advanced Options (Advanced button)
- uncheck all auth methods EXCEPT MSCHAPv2
- check 'Use Point-to-Point encryption (MPPE)'
- leave Security set at 'All Available (Default)'
- trying to force encryption level causes this option to become unset
- check 'Allow stateful inspection'
- uncheck 'Allow BSD Data Compression'
- uncheck 'Allow Deflate Data Compression'
- uncheck 'Use TCP Header Compression'
- uncheck 'Send PPP Echo Packets' (although connection works either checked or unchecked)
- save configuration
- enter password in login box
- DO NOT check either password save box at this time
- once connection establishes, verify remote connectivity - ping, rdp, ssh, etc.
- disconnect VPN session
- enter password in login box
- check both password save option boxes
- once again verify remote connectivity
- disconnect VPN session
- VPN session should automatically connect using saved auth credentials
- Create new PPTP connection
- VPNC VPN Configuration - This setup works connecting to an ASA5510 - software version 8.2(1). I didn't have any other Cisco devices to test against.
- Create new VPNC connection
- set connection name
- set Gateway
- set Group Name
- set User Password to 'Saved' and enter password
- set Group Password to 'Saved' and enter password
- set username
- set domain (if applicable)
- leave Encryption Method at 'Secure (Default)'
- set NAT traversal to 'NAT-T'
- save configuration
- open VPNC connection
- if prompted, select 'Always Allow' if you want connection to be automatic
- verify remote connectivity - ping, rdp, ssh, etc.
- disconnect VPN session
- open VPNC connection - session should automatically connect
- Create new VPNC connection
OpenConnect VPN Configuration - This setup works connecting to an ASA5510 - software version 8.2(1). I didn't have any other Cisco devices to test against.
Create new OpenConnect connection
- set connection name
- set Gateway
- set Authentication type to 'Password/SecurID'
no need to set username, OpenConnect won't store it yet
- save configuration
- open VPN connection
- check 'Automatically start connecting next time'
- click Close
- you will get the 'No Valid VPN Secrets' VPN failure message
- open VPN connection
- accept certificate (if prompted)
- change Group (if necessary)
- enter username (may need to be domainusername)
- enter password
- click Login
- if VPN connection fails, see note below
- verify remote connectivity - ping, rdp, ssh, etc.
- disconnect session
- open VPN connection
- enter password
- session should connect
Note: If you get the 'Login Failed' message, cancel and wait 15-30 minutes before attempting to connect again. Also, I ended up having to use the NT style domainusername pair for authentication, even though a Cisco AnyConnect client connecting to the same ASA only requires username.
More Detail: OpenConnect has been brutal to get connected. I got failed attempt after failed attempt. When I checked the NPS (IAS) log and the Security Event log on the W2K8 domain controller, I could see my user account authenticating properly via RADIUS from the ASA. Yet the OpenConnect client came back with a 'Login Failed' message. I'm not an ASA expert, so I have no idea what to check in the ASA configuration to troubleshoot this problem, other than the basic AAA configuration. But I believe the problem lies in the ASA configuration because when I get the OpenConnect 'Login Failed' message, the AnyConnect client from my Windows laptop fails as well. I think it may be a ridiculously short timeout or max failure setting. Whatever the issue is, I have to wait for some length of time (~15-30 minutes) for whatever the problem is to reset.
However, once I finally get the OpenConnect client to successfully connect, it worked from then on. (Just don't mess with the connection configuration, or you will get to go thru this whole process again.)
VPN setup in Ubuntu 10.04
Ubuntu 10.04 comes preinstalled with VPN support.
This features is available under the networks connections tab.
Cisco Anyconnect Linux Client
VPN (last edited 2015-05-21 10:52:58 by waldyrious)
